
Risk Factors Of Heart Diseases :
There are several risk factors for heart disease, some of which can be modified or controlled, while others cannot. Here are the most common risk factors for heart disease:
-
Age: The risk of heart disease increases with age.
-
Gender: Men are more likely than women to develop heart disease, although the risk for women increases after menopause.
-
Family history: If a close family member, such as a parent or sibling, has had heart disease, the risk is higher.
-
High blood pressure: High blood pressure, or hypertension, can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease.
-
High cholesterol: High levels of LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and low levels of HDL (“good”) cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
-
Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease, as it damages the blood vessels and can lead to the buildup of plaque.
-
Diabetes: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease by damaging blood vessels and increasing the risk of high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Read more
-
Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of heart disease, as it can lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
-
Physical inactivity: Lack of regular physical activity can increase the risk of heart disease by contributing to obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
-
Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to heart disease by increasing blood pressure and damaging blood vessels.
It’s important to note that while some of these risk factors cannot be controlled, many can be managed or modified through lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and quitting smoking.
10 Types Of Heart Diseases :
There are several types of heart disease, which can affect the heart and the blood vessels that supply it. Here are some of the most common types of heart disease:
1 . Coronary artery disease:
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of heart disease, and it occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrow or blocked due to a buildup of plaque. Plaque is made up of cholesterol, fat, and other substances that can accumulate on the walls of the arteries over time. As the arteries become narrow or blocked, the heart may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, which can lead to chest pain (angina) or a heart attack.
Risk factors for coronary artery disease :
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol
- smoking
- diabetes
- obesity
- physical inactivity
- family history of heart disease
- age
- men are also at higher risk for CAD than women, although women’s risk increases after menopause.
Treatment for CAD :
- lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet,
- getting regular exercise,
- quitting smoking,
- managing stress
- Medications such as statins, beta-blockers, and aspirin may also be used to reduce the risk of heart attack or stroke.
- In some cases, medical procedures such as angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery may be necessary to open up blocked arteries and
- restore blood flow to the heart. Early detection and management of CAD are important for preventing complications and improving outcomes.
2 . Heart failure:
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can occur when the heart muscle is weakened or damaged, or when the heart becomes stiff and less able to relax and fill with blood. Heart failure can affect either the left side, the right side, or both sides of the heart.
Symptoms of heart failure: .
- shortness of breath
- fatigue
- swelling in the legs or ankles
- rapid or irregular heartbeat
- coughing
- wheezing
- difficulty exercising or performing daily activities These symptoms can worsen over time and can lead to complications such as kidney damage, liver damage, or heart attack.
Risk factors for heart failure:
- include coronary artery disease
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- obesity
- smoking
- alcohol use
- a history of heart attack or heart valve disease
- Certain medical conditions such as thyroid disorders, sleep apnea, and kidney disease can also increase the risk of heart failure.
Treatment for heart failure :
- medications such as ACE inhibitors
- beta-blockers
- diuretics to help manage symptoms and improve heart function
- Lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet
- getting regular exercise
- quitting smoking
- managing stress can also be beneficial
- In some cases, medical procedures such as implantable devices or heart surgery may be necessary to improve heart function or treat underlying conditions.
Early detection and management of heart failure are important for preventing complications and improving outcomes. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is recommended for individuals with heart failure to ensure that their treatment plan is working effectively.
3. Arrhythmias:
Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that can occur when the electrical impulses that regulate the heartbeat are disrupted. Arrhythmias can cause the heart to beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregularly. Some arrhythmias are harmless and may not cause any symptoms, while others can be serious and lead to complications such as blood clots, stroke, or sudden cardiac arrest.
Risk factors for arrhythmic heart disease :
- coronary artery disease
- heart valve disease
- heart failure
- high blood pressure
- congenital heart defects
- sleep apnea
- diabetes
- and a family history of arrhythmias or sudden cardiac arrest
- Certain medications or substances such as caffeine, alcohol, and illicit drugs can also trigger arrhythmias.
Symptoms of arrhythmias :
- palpitations
- dizziness
- lightheadedness
- chest pain
- shortness of breath
- fainting
Diagnosis of arrhythmia : may involve tests such as electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor, or event monitor to record the heart’s electrical activity over time.
Treatment for arrhythmias :
- medications to help control the heart rhythm
- medical procedures such as cardioversion or ablation to correct the heart rhythm
- implantable devices such as pacemakers or defibrillators to regulate the heart’s electrical impulses
- Lifestyle changes such as reducing stress
- getting regular exercise
- avoiding triggers such as caffeine or alcohol may also be helpful in managing arrhythmias.
Early detection and management of arrhythmias are important for preventing complications and improving outcomes. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is recommended for individuals with arrhythmias to ensure that their treatment plan is working effectively.
4. Heart valve disease:
Symptoms of heart valve disease :
shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, dizziness, fainting, and swollen feet or ankles. Depending on the severity of the valve damage, some individuals may not experience any symptoms.
Risk factors for heart valve disease:
age, family history of valve disease, previous heart attack or heart valve infection, and certain medical conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and connective tissue disorders.
Treatment for heart valve disease:
medication to help manage symptoms or prevent complications, or medical procedures such as valve repair or replacement surgery. Valve replacement surgery involves replacing the damaged valve with an artificial valve or a biological valve made from animal tissue.
Early detection and management of heart valve disease are important for preventing complications and improving outcomes. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is recommended for individuals with heart valve disease to ensure that their treatment plan is working effectively.
5. Congenital heart defects:
Congenital heart defects are structural abnormalities present at birth that affect the heart’s structure and function. These defects can range from mild to severe and may involve abnormalities in the heart’s walls, valves, or blood vessels. Congenital heart defects occur during fetal development and may be caused by genetic or environmental factors.
Symptoms of congenital heart defects :
may vary depending on the type and severity of the defect. Some defects may not cause any symptoms, while others may cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, cyanosis (bluish tint to the skin), poor feeding or growth, and recurrent infections.
Risk factors for congenital heart defects:
include family history of heart defects, maternal exposure to certain medications or illnesses during pregnancy, maternal alcohol or drug abuse during pregnancy, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes or obesity.
Treatment for congenital heart defects:
depends on the type and severity of the defect. Some defects may not require treatment, while others may require medication or medical procedures such as surgery or catheter-based interventions to correct the defect. Treatment may also involve managing symptoms and preventing complications such as heart failure or arrhythmias.
Early detection and management of congenital heart defects are important for improving outcomes and preventing complications. Many congenital heart defects can be detected during routine prenatal ultrasounds, and early diagnosis and treatment can lead to better outcomes for affected individuals.
6. Cardiomyopathy:
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle, where the heart becomes enlarged, thickened, or stiff, and is unable to function properly. There are several types of cardiomyopathy, including:
- Dilated cardiomyopathy: The heart becomes enlarged and weakened, making it difficult for it to pump blood effectively.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: The walls of the heart become thickened, which can cause problems with the heart’s ability to pump blood.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy: The heart becomes stiff and has trouble filling with blood.
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: The muscle tissue in the right ventricle of the heart is replaced by fatty tissue, which can lead to abnormal heart rhythms.
The causes of cardiomyopathy can include genetic factors, infections, and certain medications, among other factors. Symptoms of cardiomyopathy can include shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and swelling in the legs and feet. Treatment options for cardiomyopathy can include medications, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgery or other procedures.
7. Pericarditis:
Pericarditis is a heart disease characterized by inflammation of the pericardium, which is the thin, double-layered sac that surrounds the heart. This inflammation can cause chest pain and discomfort, as well as other symptoms.
The most common cause of pericarditis is a viral infection, but it can also be caused by bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, certain medications, and other medical conditions. Symptoms of pericarditis can include sharp chest pain that may be worse when lying down or taking deep breaths, fever, shortness of breath, and a dry cough.
Treatment for pericarditis depends on the underlying cause of the inflammation, but may include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammation and relieve pain, colchicine to reduce inflammation and prevent recurrences, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation in more severe cases, and antibiotics if there is a bacterial infection. In some cases, a procedure called pericardiocentesis may be necessary to drain excess fluid that has accumulated around the heart.
8. Aortic aneurysm:
An aortic aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of the aorta, which can be life-threatening if it ruptures. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including high blood pressure, smoking, and genetics.
9. Myocarditis:
Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle, which can be caused by infections or autoimmune disorders.
10. Heart attack:
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot. It can lead to permanent damage to the heart muscle and even death if not treated promptly.


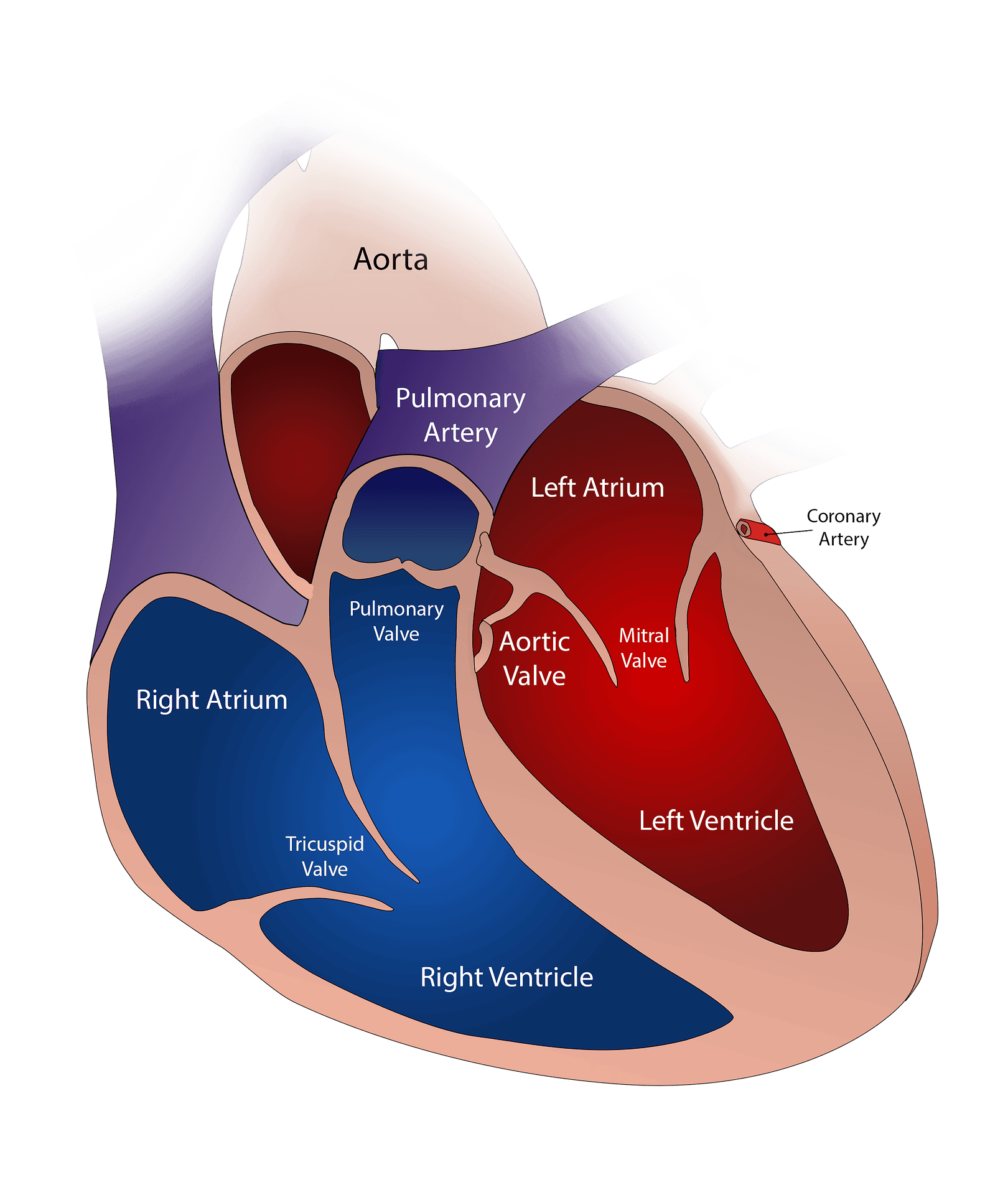
1 thought on “Heart Diseases – 10 Major Heart Issues In United States”